The Color Tolerance of LED Strip Lights
Do you understand the color temperature of the LED strip? What is the relationship between color temperature and color tolerance?
Many people are busy purchasing LED Strips every day, asking suppliers for the color temperature of the LED Strips, the requirements for the quality of the LED Strips, the requirements for various photoelectric parameters of the LED Strips, the requirements for the power of the LED Strips, etc.
However, few people will mention the need for the SDCM of the LED Strips and the requirements for the consistency of the light color.
So when it comes to this, there will be a problem. What is the relationship between color temperature and SDCM? What is the importance of SDCM for light strips? Knowing this will help you to make a right and professional LED procurement plan to fulfil your purchasing needs.
Read on to find out more about this information.
#1. What is the color temperature?
#2. What is the consistent color temperature CCT?
#3. What is the color tolerance?
#4. What is the relationship between color tolerance and color temperature?
#5. What is the relationship between color tolerance and color difference?
#6. Color tolerance international industry standards
#7. The impact of international standards on color tolerance
#8. The effect of color tolerance on the lighting quality of LED strips
#9. How to test the color tolerance of LED strips
CHAPTER 1:
What Is The Color Temperature?
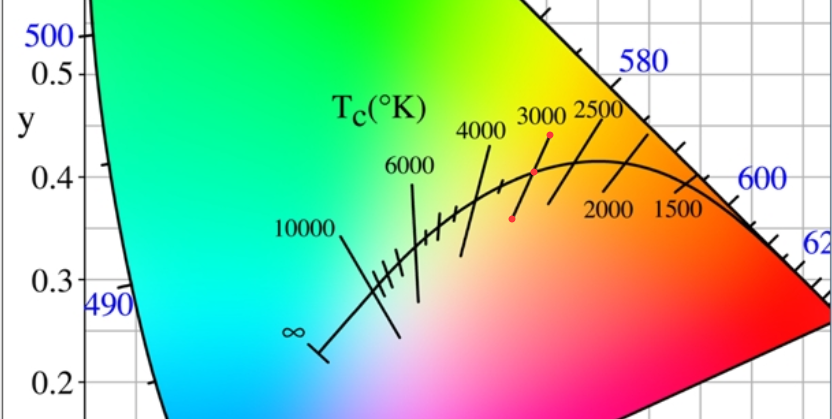
When a black-body is heated to a temperature, and the color of black-body emitted is the same as the color of the light emitted by a particular light source, the temperature at which the black body is heated is called the color temperature of the light source, that is, the color temperature.
The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of comparable color to that of the light source.
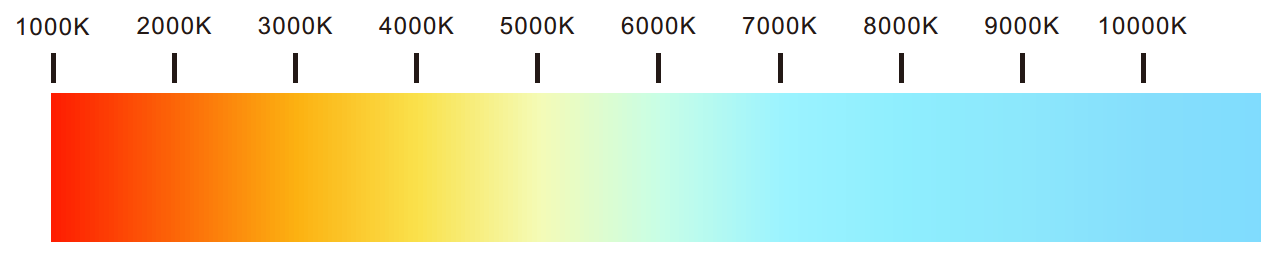
When the standard black body is heated, the color will start from deep red->light red->orange->white->blue light when the temperature rises to a certain level.
In the era of traditional light sources, the color temperature difference between the light sources is 150K, and it is easy for the human eye to find the difference between them, but now the LED era is different.

Warm white color
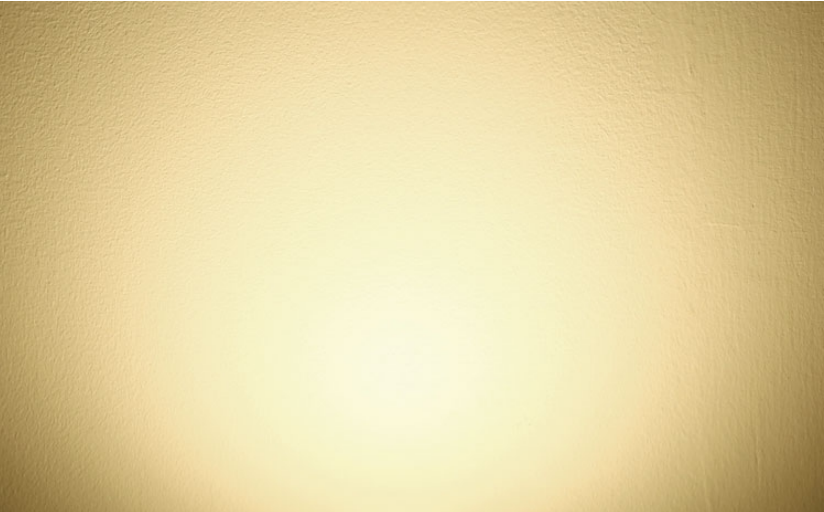

Color Greenish
It is obvious that the above two colors are different. The light spot on the left is white, while the light on the right is green.
So what are their color temperatures? Is there a difference of 150K? Don’t worry, please refer to the following data:

CCT = 3061K

CCT = 3078K
▲ According to the data, the difference between these two color temperature is only 17K, and not as large as 150K.
Some people may doubt that why their color temperature difference is too less, but the human eye can see the difference in light color between them?
Read on to find out more about this information.
CHAPTER 2:
What Is Correlated Color Temperature (CCT)?

Everyone should be able to see the data tested. It is the correlated color temperature(CCT), not the color temperature. Is there a difference between them? Of course, there are.
The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of comparable color to that of the light source.
In other words, it can only be called the color temperature when it falls on the black body radiation line.
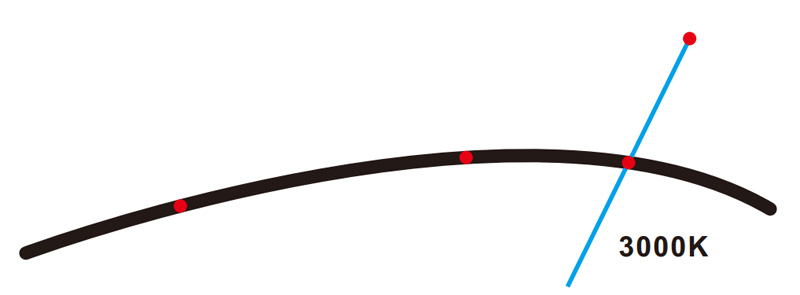
Black body radiation line
Correlated color temperature and color coordinate conversion formula:
T=-437n3+3601n2-6861n+5514.31,n=(x-0.3320)/(y-0.1858)
T (Color Temperature)
N(coefficient)
X,Y (Color coordinates)
From the formula and definition:
1. The color temperature and color coordinates are one-to-many relationships, and the same color temperature has different XY values;
2. The same color temperature produces different color senses.
3. The two points in Figure AB below are the same color temperature, but they show completely different colors.
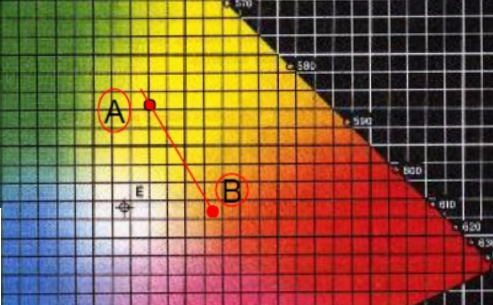
It means that the light from the light source, which is emitted from the black body radiation at 3000K, has been deviated, but 3000K can only be described on this line. Then this happens:


▲ One color is greenish, and the other color is reddish. Although they are different from the human eye, both of them are called 3000K.
It can be concluded that the correlated color temperature is an interval, and the color temperature value in this interval fluctuates within a range.
Perhaps many people will be confused, and there are many XY combinations of the same color temperature, what color temperature and coordinates are in line with solid-state lighting and human eye sensory comfort? How can it be solved?
This is necessary to have our protagonist: SDCM (Standard Deviation of Color Matching)
CHAPTER 3:
What Is SDCM (Standard Deviation of Color Matching)?
McAdam Ellipse Theory:
In 1942, scientist McAdam experimented with 25 colors using the relevant principle, measuring about 5 to 9 opposite sides of each color point, recording the two points when they were able to distinguish the color difference. The result was some An ellipse of varying sizes and lengths, called the MacAdam ellipse.
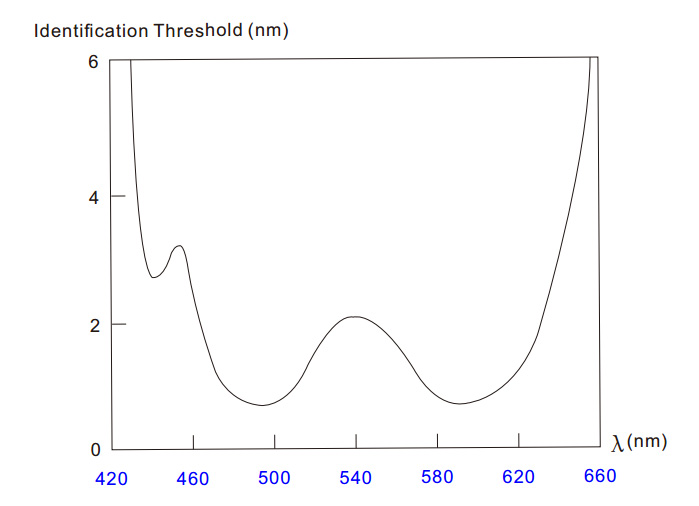
Human eye sensitivity to color
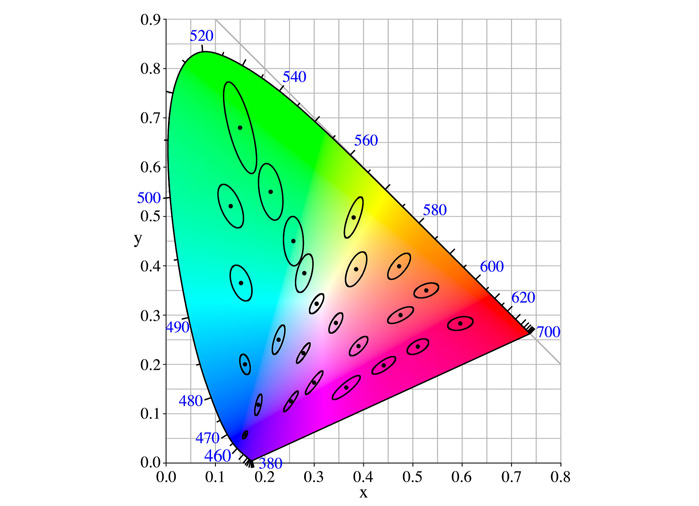
McAdam Ellipse Theor
From the above figure, the sensitivity curve of the human eye to color:
1. The difference in sensitivity of the human eye to the color of the spectrum is non-uniform;
2. According to the recognition of the color of the human eye, the size of the MacAdam ellipse is also inconsistent in different regions.
McAdam’s ellipse theory: provides a guide to the accuracy of color vision and the goodness of distinguishing similar colors. The color inside the ellipse represents a range in which the human eye does not feel that the color changes too much, which is called the full capacity of the color.
So, in the actual application, how do we quantify the vast capacity of color?
Here, we introduce a concept: SDCM (Standard Deviation of Color Matching).
SDCM: Characterizes the difference between the X and Y values calculated by the optical color detection system software and the standard light source. The smaller the amount, the closer the product’s light color coordinate to the standard value, the lower the difference between the spectrum emitted by the light source and the usual range, the higher the accuracy, the purer the color of the light.
Known by the definition of SDCM:
a. The color tolerance actually refers to the distance of the measured value from the target value;
b. An ellipse generally characterizes quantification of color tolerance.
Unit: SDCM (Standard Deviation of Color Matching):
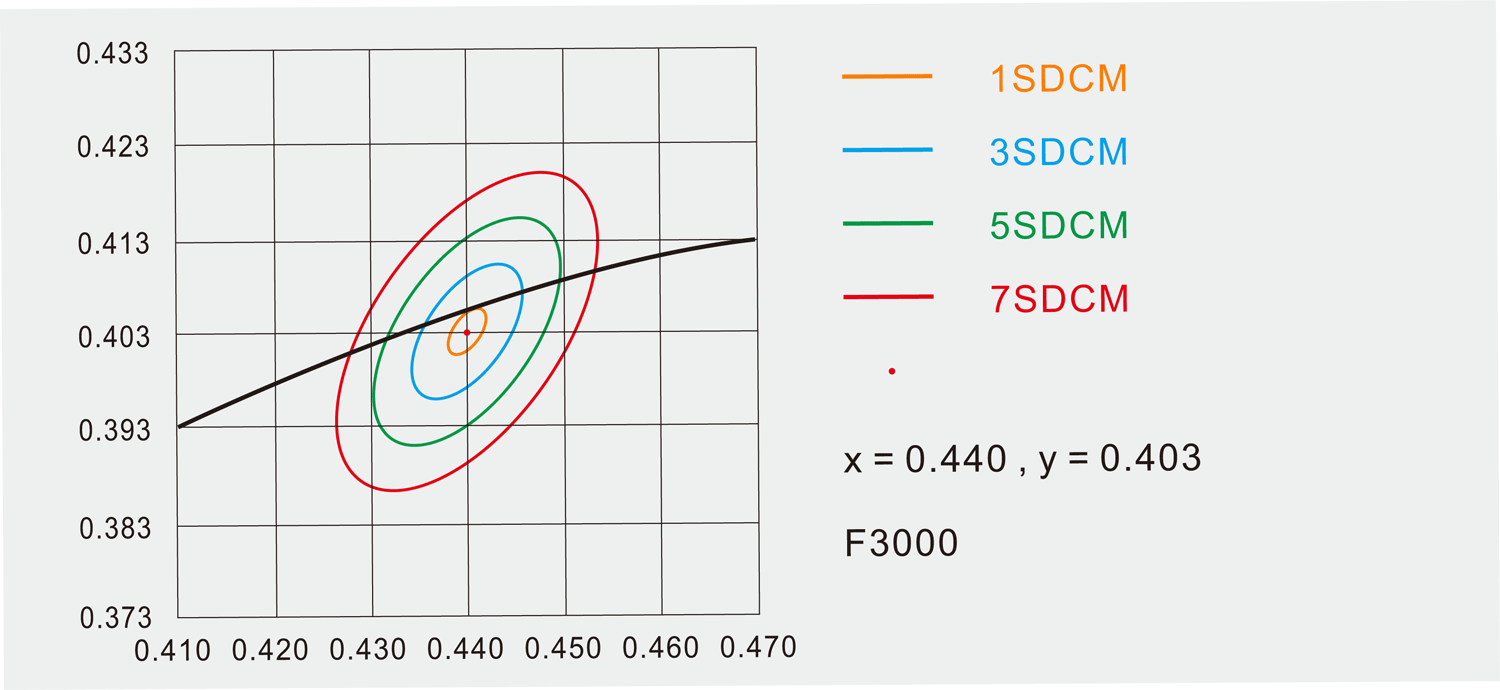 ▲ The ellipse in the above illustration can be understood as Step, you can understand it like this: 3SDCM = 3 Steps. Usually, the human eye can find the difference in 5~7 steps. That is to say, when SDCM between the light sources is higher than five steps, it will be easily recognized by human eyes.
▲ The ellipse in the above illustration can be understood as Step, you can understand it like this: 3SDCM = 3 Steps. Usually, the human eye can find the difference in 5~7 steps. That is to say, when SDCM between the light sources is higher than five steps, it will be easily recognized by human eyes.
CHAPTER 4:
What’s The Relationship Between SDCM and CCT?
Now let’s take a look at the two light sources we said at the beginning:
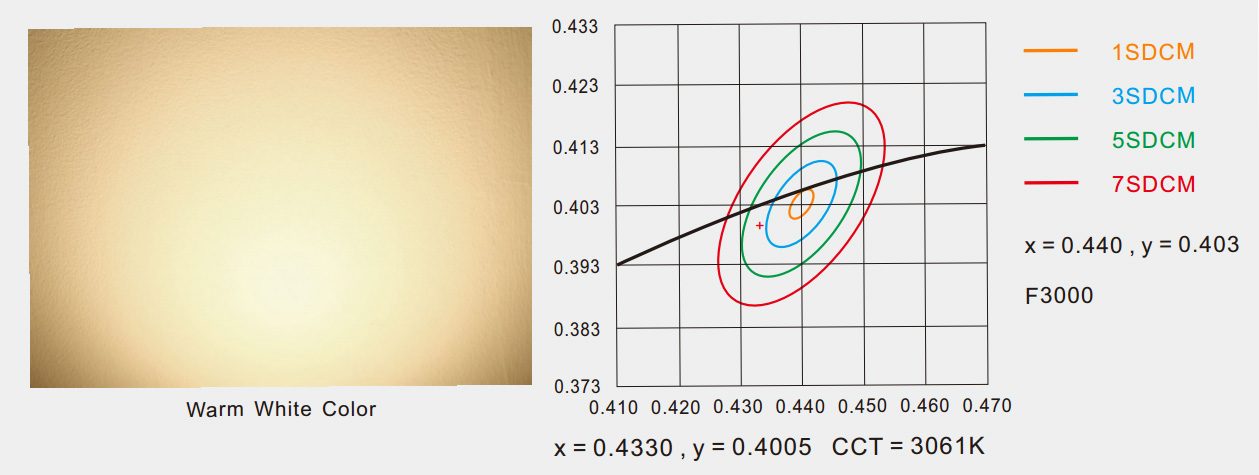
▲ Warm white CCT=3061K, it can be seen from the figure that the SDCM between it and the standard light source is within 5 SDCM, which is SDCM<5.

▲ Greenish warm white CCT=3078K, which is very different from the above 3061K color temperature value.
The SDCM between it and the standard 3000K is already outside 5 SDCM, which is SDCM>7, and the color temperature deviation is too large. There is already a color difference between them.
CHAPTER 5:
What’s the relationship between Chromatic Aberration(Color Difference) and SDCM?
Chromatic Aberration: It is the difference of colors, that is, the difference between the X and Y coordinate values of the two light colors. The smaller the gap, the lower the chromatic aberration.
SDCM: It is the difference between the X and Y values of the product and the X and Y values of the standard light source. The smaller the distance, the lower the SDCM
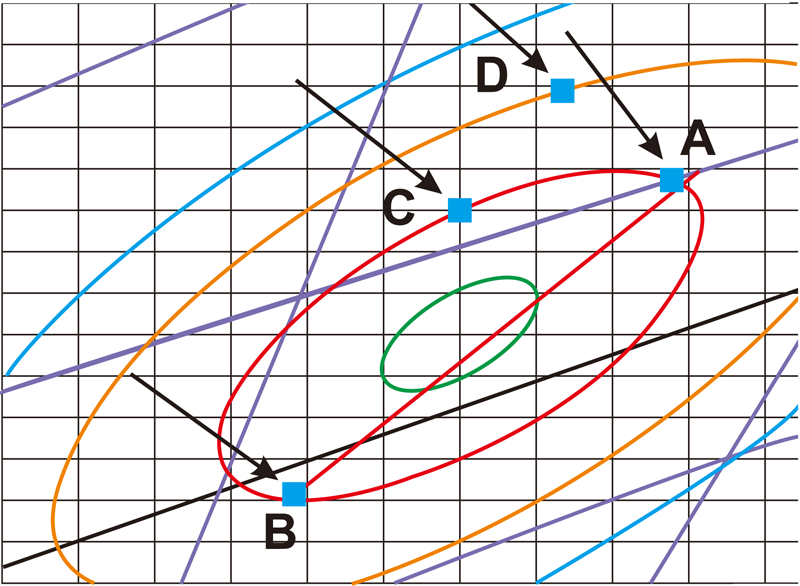
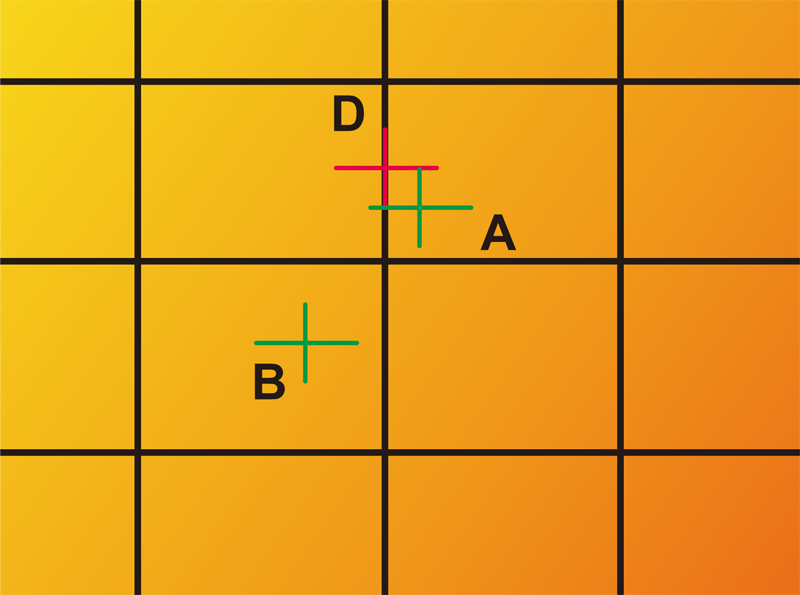
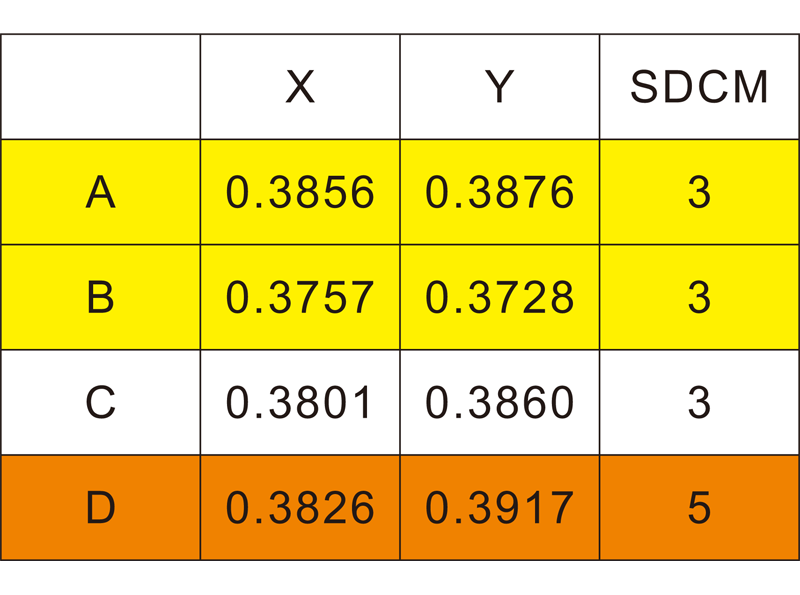
Here is an example: A (sample) is 3 SDCM, B is 3 SDCM, D is 5 SDCM, and the x coordinate value of A is subtracted from the x coordinate value of B. The result is equal to +0.0099. The same algorithm, the difference of y coordinates is equal to +0.0148, which means that the chromatic aberration of A-B is (X=+0.0099, Y=+0.0148), and the chromatic aberration of A-D is (X=+0.0030, Y=-0.0041).
It shows that the chromatic aberration between A and B is greater than the difference between A and D, but the SDCM of A and B are equal, both are 3SDCM, and the SDCM of A and D is different by 2, so SDCM and chromatic aberration are different.
The following figure shows the chromatic aberration of the light emitted by MacAdam’s 7-step, 5-step, 3-step, and 2-step ellipse at 3000K color temperature:
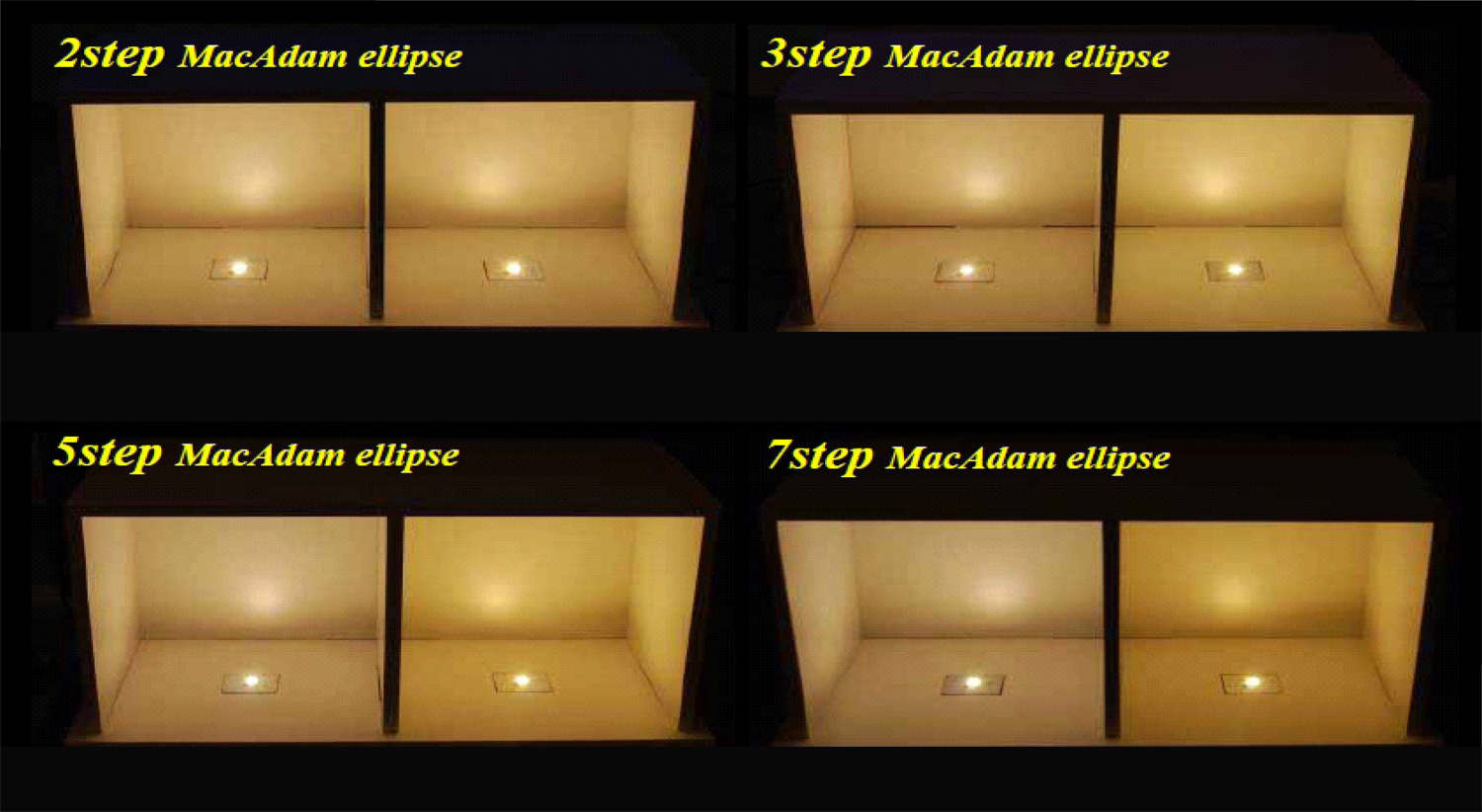

It can be seen from the above comparison chart:
1. McAdam’s 2-step ellipse can not see the chromatic aberration by the human eye; the 3-step ellipse chromatic aberration is small; the 5-step and 7-step chromatic aberration are more obvious.
2. 3 step ellipse is the critical value of human eye recognition.
McAdam’s experiment proved that there is a linear relationship between the just noticed chromatic aberration and color matched standard deviation, and three times of the standard deviation (that is, the position of the three steps) is the just noticeable difference of the chromatic aberration. If the two color coordinates fall within the 2nd MacAdam ellipse (that is, within two levels), then the human eye can hardly see the difference between the two colors.
The difference between the color corresponding to the 3rd MacAdam ellipse boundary and the center color of the 3rd MacAdam ellipse is the chromatic aberration that the human eye can detect, and the larger the SDCM is, the larger the chromatic aberration is.
SDCM is the difference between the x and y values between the measured source and the standard source. The smaller the gap, the lower the SDCM. Then: Where does this standard light source come from? Who made this standard?
CHAPTER 6:
LED Industry SDCM Standard
There are three main types of SDCM standards in the world:
1. North American Energy Star Standard
Energy Star ANSI C78.376, color tolerance ≤ 7 SDCM, divided by LED characteristics.
2. EU IEC standard
EU standard ERP, color tolerance ≤ 6 SDCM, according to the technical requirements to regulate the LED division area.
3. Chinese GB standard
Chinese standard GB10682-2002, double-end fluorescent lamp performance requirements color tolerance ≤ 5 SDCM, can be used as a reference for LED lamp color tolerance.
The coordinate values of the standard color temperature SDCM center corresponding to the North American ANSI standard and the European Union IEC standard are summarized as follows:
IEC 60081 Document Download: BS-EN-60081-1998 IEC-60081-1997
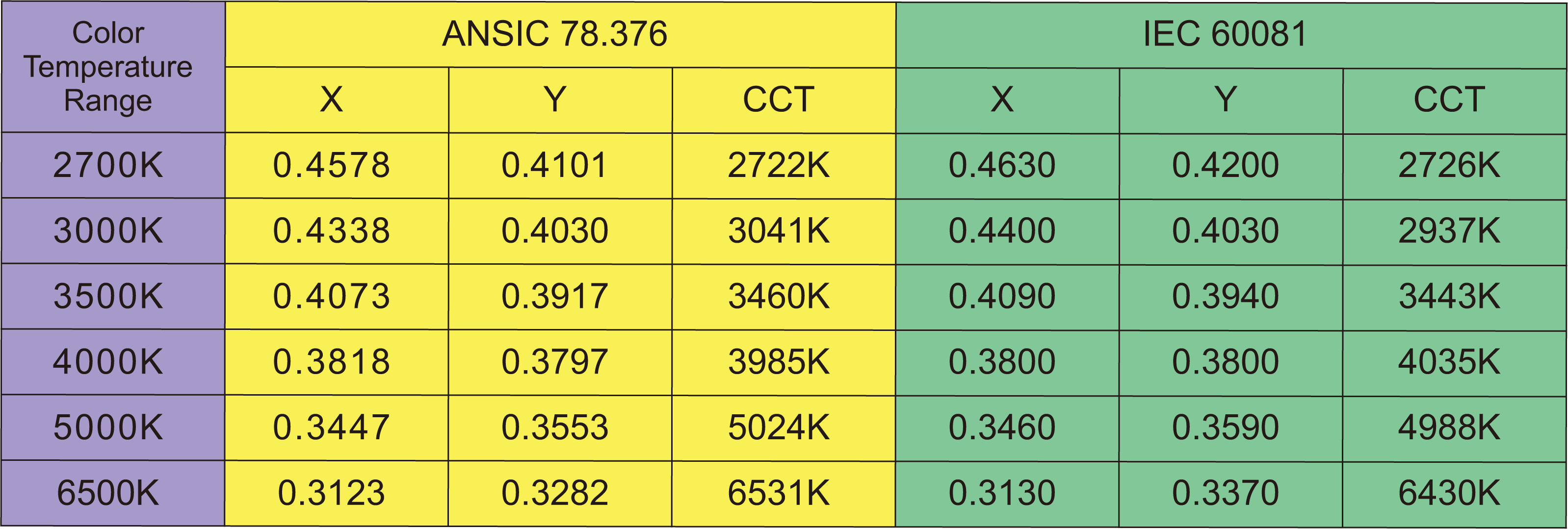
The following are the standard color temperatures of ANSI and IEC standards, and the corresponding color temperature coverage in the three steps, five steps, and seven steps SDCM ranges.
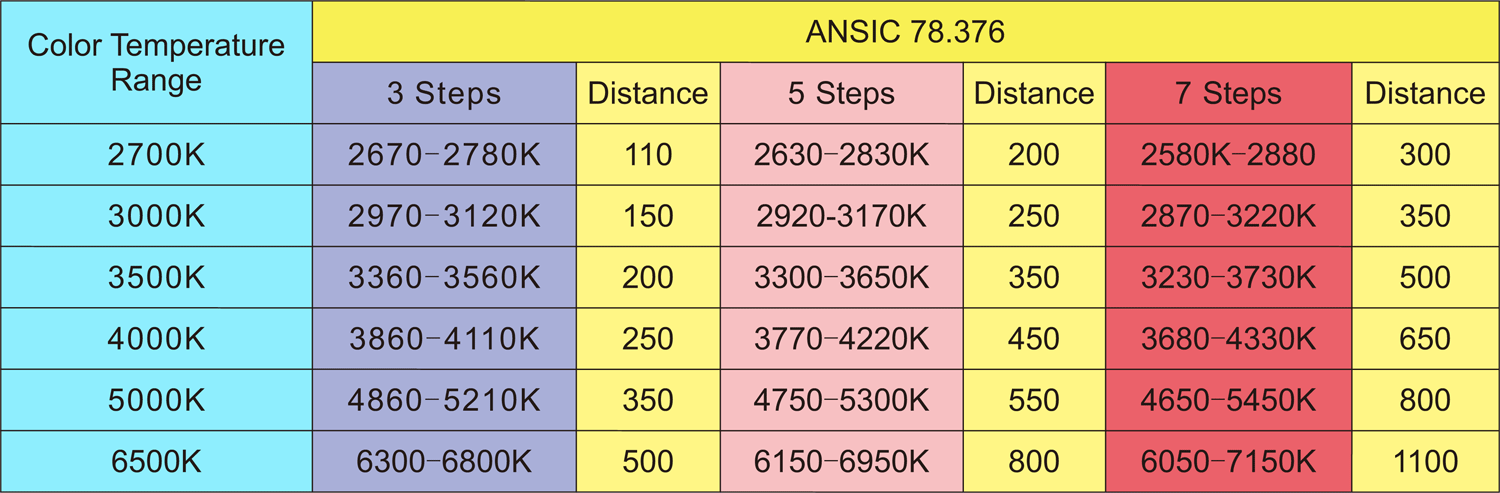

If you want 2700K standard color temperature, the CCT must be controlled within the range of 2680-2790K when it is based on ANSIC standard and SDCM<3.
It can be seen from the above chart data that the SDCM coordinate of the two standard color temperatures are different, and the range of correlated color temperatures covered is varied.
This makes a difference in the determination of the standard color temperature, so we need to determine the SDCM standard based on our actual situation and demand. Then, while referring to the standard, how do we confirm the relevant color temperature range that we need, and give a reasonable correlation color temperature interval value?
CHAPTER 7:
The Impact of International Standard on SDCM
The following is a 3rd-order comparison diagram of the IEC standard and the ANSI standard.
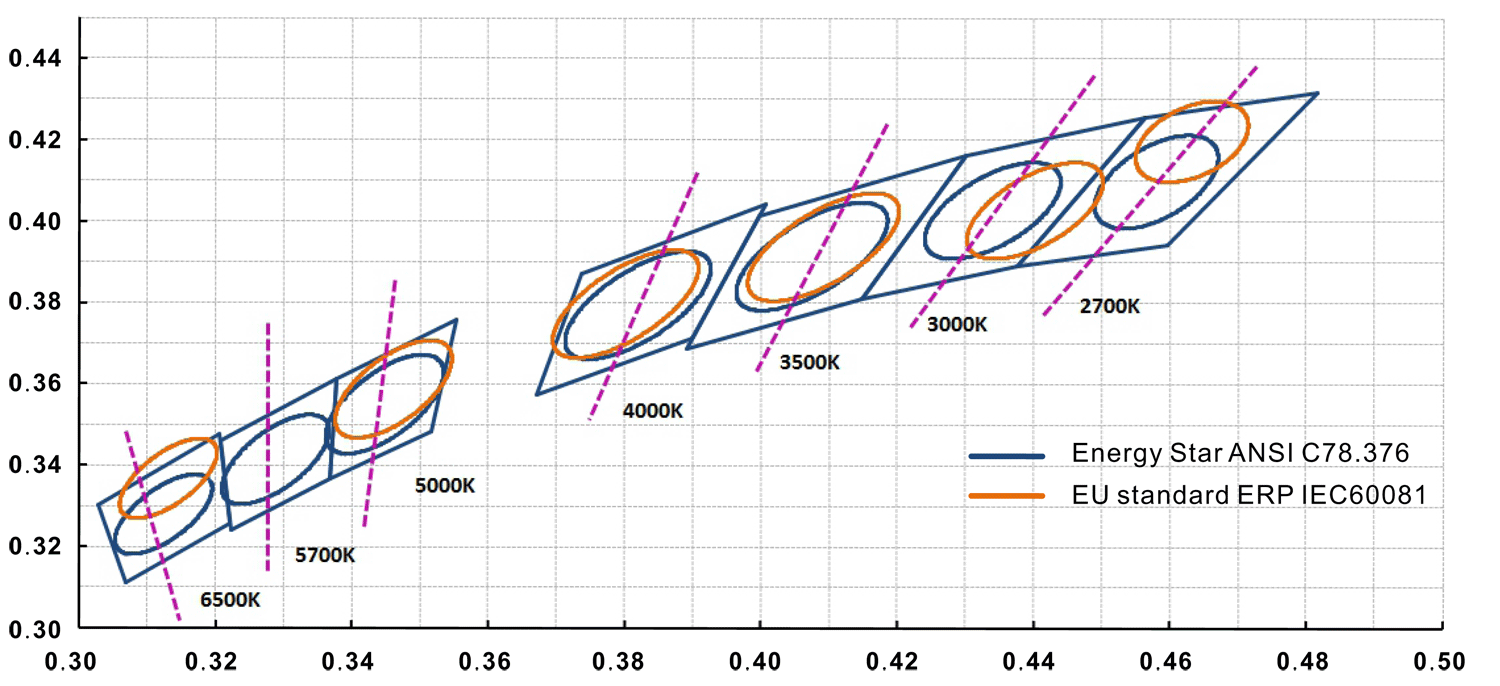
1. It can be seen from the figure that the standard color temperature coordinate center points of IEC and ANSI standards are different, and the difference of 6500K, 3000K, and 2700K is the most obvious.
So you must first confirm with the supplier what standard to use as a reference when you place the order. (DERUN LIGHTING USE EUROPEAN STANDARD)
2. The correspondence between color temperature and SDCM causes some problems:
When referring to the standard color temperature versus color, due to the interval constraint of the color temperature of each standard SDCM of the standard color temperature, the color temperature range of the actual demand product is narrowed, resulting in unreasonable product requirements.
Example.
If the customer needs 3000-3300K, the European standard and the SDCM is less than five steps. We can find out that the relevant color temperature range required by the customer is included in both 3000K and 3500K according to the following IEC standard table.
Referring to the five steps of 3000K, it is (2820-3070K), then the range of the required requirements is only 70K (3000K-3070K). If it refers to the five steps range of 3500K, it is (3280-3630K), only about 20K (3280-3300K) color temperature, the product is difficult to meet the demand.

Therefore, the correlation color temperature range we give must be within a reasonable range, and the size of this range needs to be determined by the specific field of accuracy that the supplier can control.
3. SDCM shift problem caused by machine difference
If there is a significant deviation between the standard parts of the two suppliers, even if the SDCM is the same standard, the difference in the value of the test is still huge.
It’s not because the coordinate value of the center point of the SDCM is not the same, but the standard of the machine. The center point offset caused by the standard deviation of the device, so be sure to confirm the color again after replacing the supplier.
CHAPTER 8:
Influence of SDCM on lighting Quality of LED strip lights
The LEDs of the LED strip is linearly arranged. If there is a color difference between the led, it is easy to be recognized by the human eye, and the light color of the whole strip is inconsistent, giving a lousy lighting experience. You need to buy a light strip with higher light efficiency and smaller SDCM to getting quality lighting effect.
The advantage of SDCM
1. The LED light strip has better light color consistency and emits light more purely.
2. The inventory of different types of led strip light is confusing, and the backlog of stocks in various batches is overwhelming. Since the color temperature of each batch of led strip light is more or less different, this directly leads to the situation that different batches of strips cannot be mixed.
This increases the inventory cost of the wholesaler and also increases the inventory management workload, which is perfectly solved by the control of SDCM.
CHAPTER 9:
How to test LED Strip’s SDCM
Testing the SDCM of the LED strip needs the help of an integrating sphere machine and spectrometer machine. The followings are the SDCM test method and test report for both SMD5050 led diode and 5050 LED Strip light.
1. SMD5050 LED Diode SDCM Test:
Test Machine: small integrating Sphere machine, spectrometer machine
Test LED: SMD5050 LED Diode in warm white color
Light Source Data: CCT: 3000K
CRI: >80
Flux: 21lm

EVERFINE CAS-200 Fast Spectrometer / Small Integral Ball
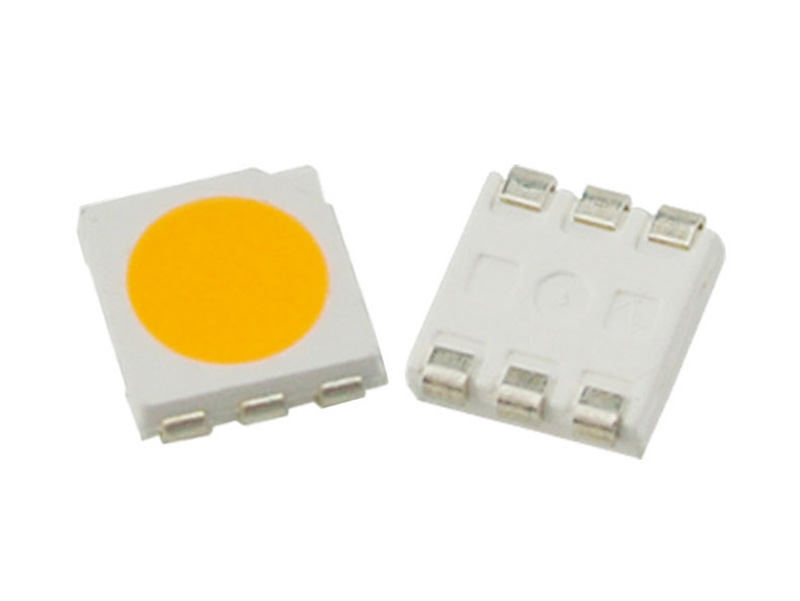

SMD5050 LED Diode in warm white color
SMD5050 LED Diode Test Report
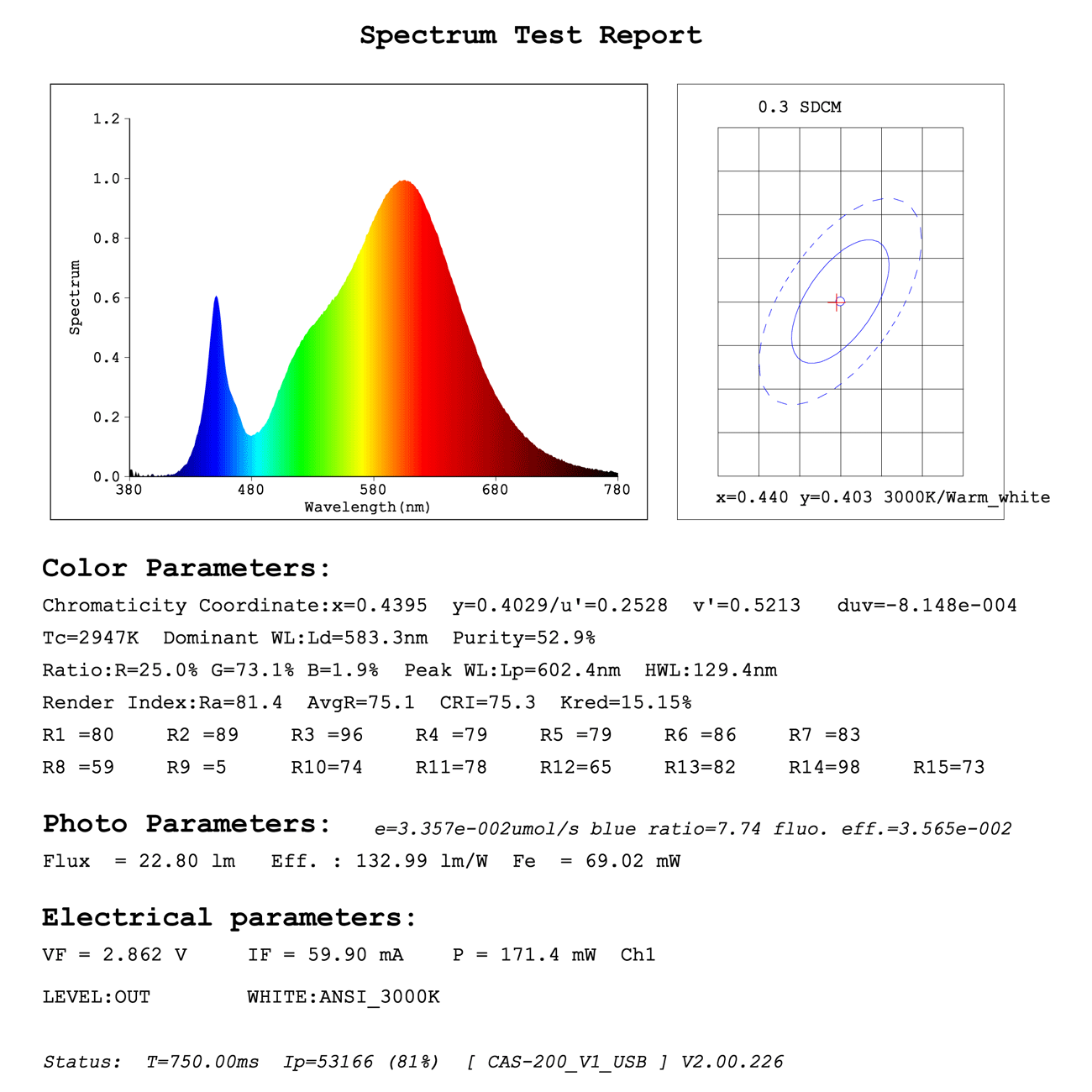
As can be seen from the SDCM result in the upper right corner of the test report, the SDCM of the light source is 1.9SDCM, which is very close to the standard color temperature value.
2. SMD5050 LED Strip Light SDCM Test:
Test Machine: big integrating Sphere machine, spectrometer machine
Test LED: SMD5050 LED Strip Light in warm white color
Light Source Data: CCT: 3000K
Flux: 600lm
Length: 50cm
LED Quantity: 30leds
EVERFINE CAS-200 Fast Spectrometer / Big Integral Ball
SMD5050 LED Strip Light in warm white color
SMD5050 LED Strip Light Test Report
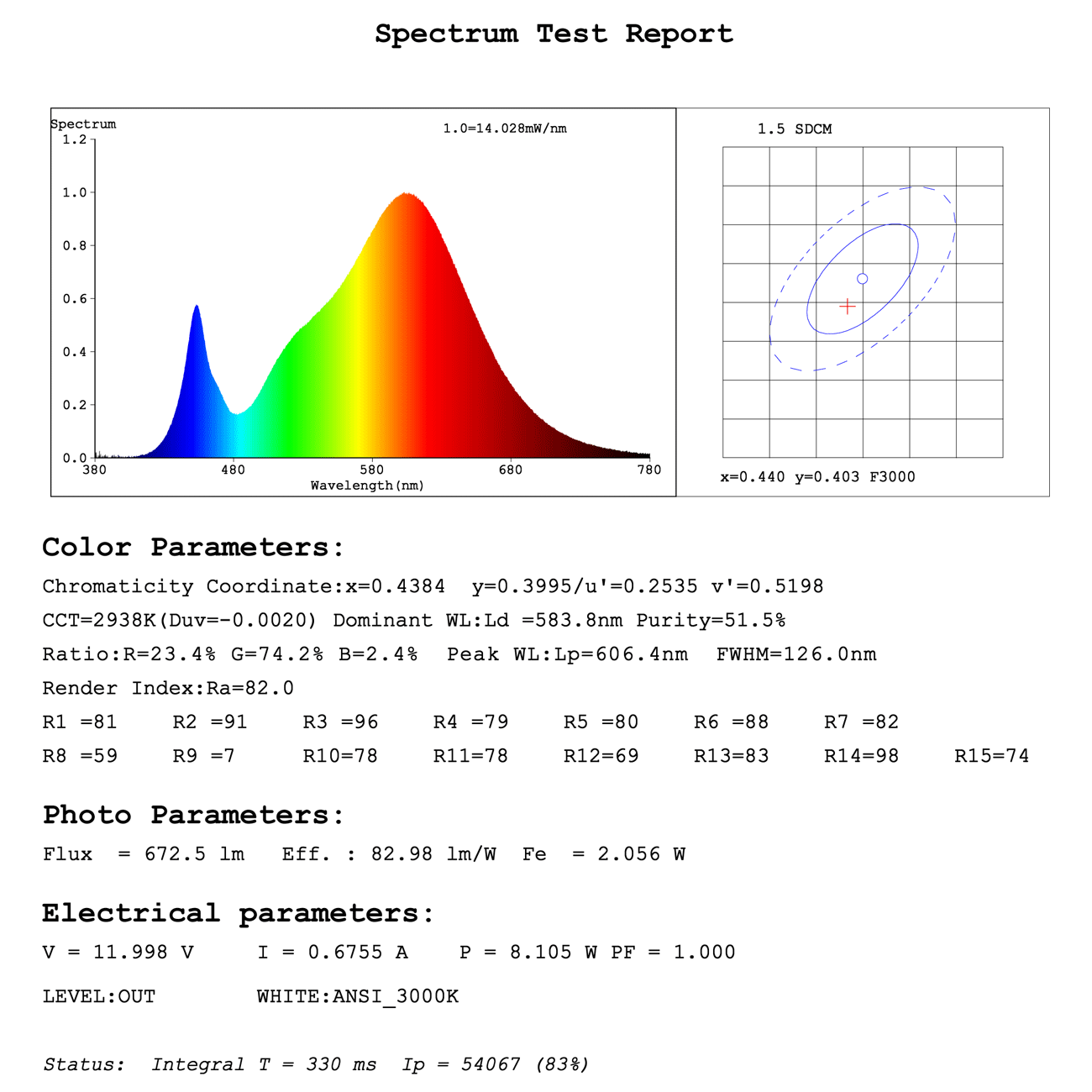
As can be seen from the SDCM result in the upper right corner of the test report, the SDCM of this led strip light is 1.5SDCM, which is very close to the standard color temperature value.